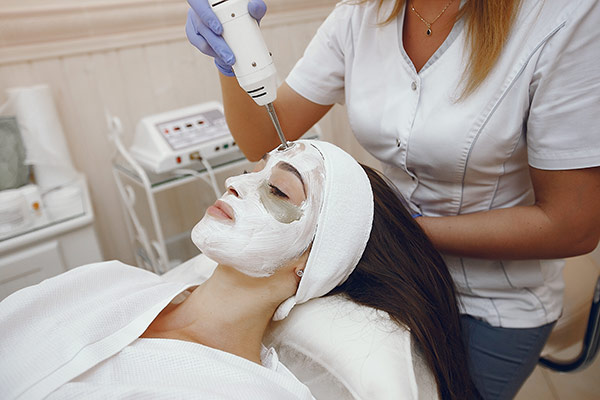
Peeling refers to a cosmetic treatment designed to improve the appearance and texture of the skin by removing its outer layers. This procedure can be performed using chemical solutions, mechanical exfoliation (such as microdermabrasion), or laser therapy. Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to the skin that causes the outer layers to peel off. The depth of the peel can range from superficial to deep, depending on the strength of the solution used. Superficial peels use mild acids like alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs), which remove only the outermost layer of skin, called the epidermis. They are often used to treat fine wrinkles, dryness, uneven skin tone, and acne. Medium peels penetrate deeper into the epidermis and dermis, using stronger agents like trichloroacetic acid (TCA). These are often used for treating deeper wrinkles, sun damage, and more pronounced pigmentation issues. Deep peels involve the use of powerful chemicals like phenol and are used to treat more severe skin concerns such as deep wrinkles, scars, and precancerous growths. These peels can lead to dramatic improvements but also require longer recovery times. Microdermabrasion is a mechanical exfoliation technique where tiny crystals or a diamond-tipped wand gently remove the outermost layer of skin. It is often used to treat mild acne scars, fine lines, and minor skin discoloration. Laser peeling, or laser resurfacing, uses focused beams of light to remove skin layer by layer. It can treat a variety of skin conditions, including wrinkles, scars, and pigmentation issues. Peeling treatments stimulate skin regeneration, revealing smoother, more youthful skin underneath. The type of peel chosen depends on the individual’s skin type, condition, and desired outcome.